Choosing the right power cable can be confusing—mixing up IEC, NEMA, and CEE standards could lead to costly compatibility issues or device failures. This guide will simplify the key differences and help you select the correct power cable for your specific needs, ensuring seamless connectivity and safety.
What are Power Cables and Power Cords?
A power cable consists of one or more electrical conductors, typically covered in an insulating layer. It is designed to carry electrical power. These cables are commonly used in permanent installations, such as transmitting electricity over long distances or in industrial and high-voltage settings.
In contrast, a power cord is a detachable, flexible cable that connects portable devices, such as computers or household appliances, to power outlets. Power cords are designed for temporary or portable connections and commonly use connectors like IEC power cords: C13/C14, NEMA power cords: 5-15P, or CEE 7/7, etc.
While both follow standards set by international organizations and can sometimes be interchanged, the key difference lies in their application: power cables are intended for fixed wiring, whereas power cords are designed for temporary or portable connections.
Materials and Configuration
Power cables are composed of several key components, each serving a specific function to ensure safe and efficient electricity transmission:
- Conductors: Typically made of copper or aluminum, conductors are responsible for carrying the electrical current. Copper is favored for its excellent conductivity and flexibility, while aluminum is chosen for its lighter weight and cost-effectiveness.
- Insulation: This layer surrounds the conductor to prevent electrical leakage and protect against short circuits. Materials such as cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) are commonly used for insulation due to their electrical properties and durability.
- Shielding: Some power cables include a shielding layer to protect against electromagnetic interference (EMI). This is particularly important in environments where external electrical noise could affect performance. Shielding materials often include metallic tapes or braids.
- Sheath/Jacket: The outermost layer protects the cable from environmental factors such as moisture, chemicals, and physical damage. Materials like PVC, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), or polyethylene are commonly used for their protective qualities.
AC Power Cords vs DC Power Cords
Power cords can be categorized based on the type of current they transmit.
AC power cords are designed to carry alternating current (AC), the standard form of electricity in most homes and commercial spaces. They are commonly used to connect household appliances and other equipment to wall outlets, adhering to standards set by IEC, NEMA, and CEE.
On the other hand, DC power cords carry direct current (DC), often used for portable devices or battery-powered equipment, such as laptops, cameras, or mobile chargers. DC cords usually connect to AC adapters or batteries that convert AC to DC, featuring barrel-type connectors or USB connections tailored for smaller electronics.
In the next section, we’ll explore the main types of AC power cords in detail based on these standards.
3 Main Types of Power Cables and Connectors
Power cables and connectors play a fundamental role in delivering alternating current (AC) power safely and efficiently to electronic devices worldwide. To ensure compatibility, safety, and standardization, three major international standards are followed for different types of power cable and their ends (connectors and plugs): IEC for global use, NEMA for North America, and CEE for European countries.
These standards define specifications for cable and connector shapes, voltage, and amperage ratings. It’s important to understand their different subcategories and types. Below, we’ll go over the details of these standards to help you choose the right options for different applications.
IEC
The IEC standard, developed by the International Electrotechnical Commission, is widely used globally. These connectors are valued for their flexible and standardized design, making them easy to use across different devices and regions. They are commonly found in electronics, IT equipment, and household appliances because their consistent structure design allows easy interchangeability between devices around the world with suitable adapters.
The most recognized IEC power connectors adhere to the IEC 60320 standard, which uses "C" codes to categorize connector types. Connectors are classified as male or female based on how they mate. Female connectors are assigned odd numbers, while compatible male connectors are designated with the next even number. This standard includes various connectors for various applications, classifying them with different numbers based on shape, amperage, and voltage ratings. These connectors come in both polarized versions (which maintain consistent live and neutral connections) and non-polarized forms.
Below are the most commonly used power connector types:
- C5/C6: Known as the "cloverleaf" or "Mickey Mouse" connector, the C5 (female) and C6 (male) pair is rated for 2.5A and up to 250V. This connector is often used in laptop power supplies, portable projectors, and other small appliances.
- C7/C8: The C7/C8 connectors, sometimes called the “figure-eight” connector, are non-polarized and rated for 2.5A and up to 250V. They’re commonly found on low-power devices like DVD players, some game consoles, and small radios. Polarized C7 connectors (with a flat side) ensure the plug is connected in a specific orientation for certain devices.
- C9/C10: The C9 (female) and C10 (male) connectors are uncommon but are rated for 6A and up to 250V. These connectors are used for select types of office equipment and smaller power-hungry devices that require moderate current.
- C13/C14: These are among the most popular IEC connectors, rated for 10A and 250V. The C13 (female) and C14 (male) connectors are standard in desktop computers, monitors, and office equipment. They are widely used in both home and data center environments due to their versatility and moderate power capacity.
- C15/C16: Similar in design to C13/C14 but rated for higher temperatures up to 120°C. These connectors, also rated for 10A and 250V, are used in applications requiring higher heat tolerance, such as electric kettles and some networking equipment.
- C19/C20: With a higher current rating of 16A at 250V, these connectors are typically used for more demanding equipment, like servers, data center hardware, and heavy-duty appliances.
- C21/C22: These are designed for high-temperature applications, with a maximum operating temperature of 155°C. These connectors are suitable for high-power, heat-generating devices, often used in industrial or specialized equipment.
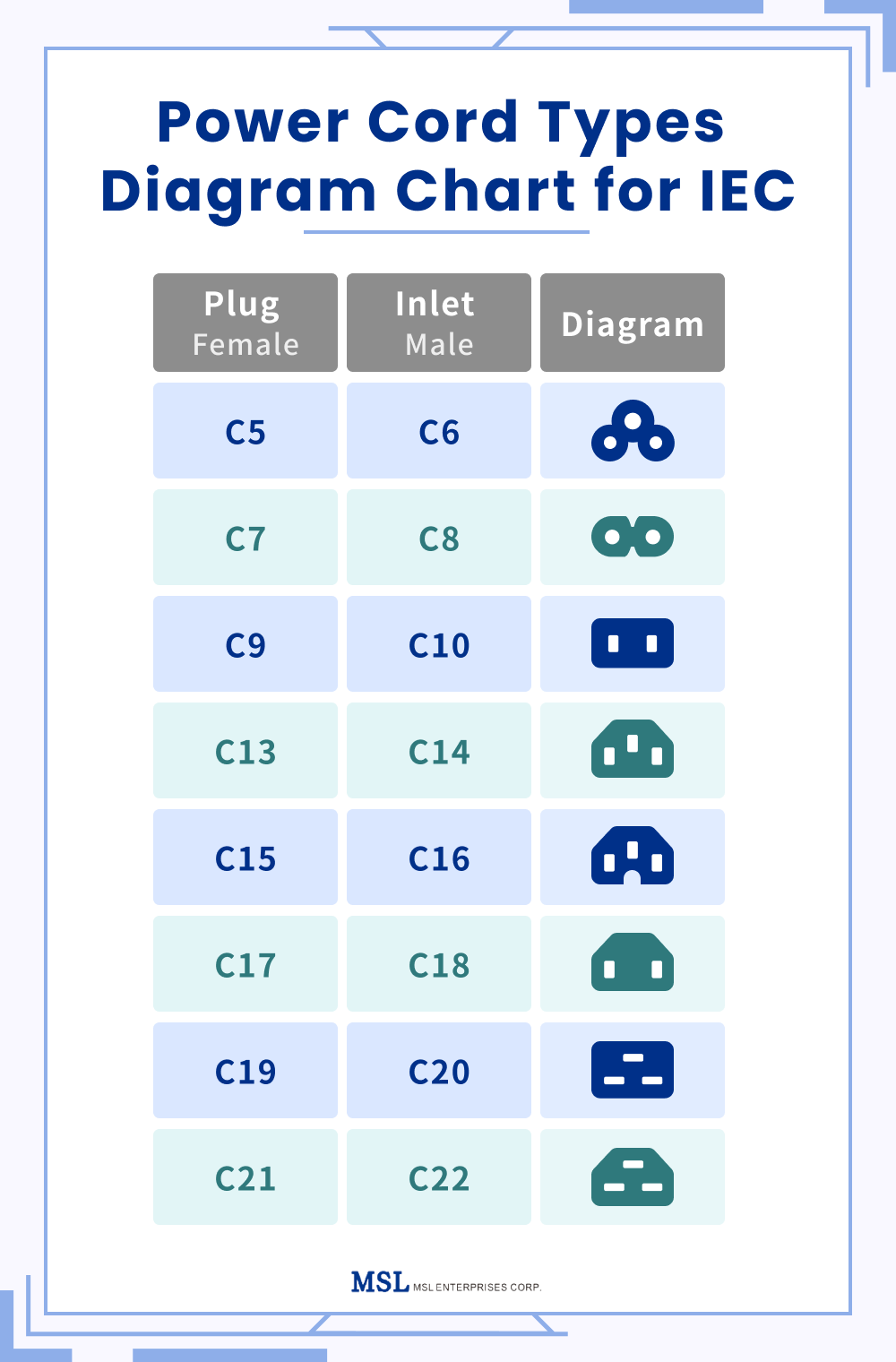
Power Cord Types Chart for IEC
| Connector Pair (Female/Male) | Earth Contact | Max Current (Global) | Max Voltage (Global) | Max Current (North America) | Max Voltage (North America) |
Max Temperature | Polarized |
| C5 / C6 | Yes | 2.5A | 250V | 2.5A | 125V | 70°C | No |
| C7 / C8 | No | 2.5A | 250V | 2.5A | 125V | 70°C | Yes (Polarized C7 available) |
| C9 / C10 | Yes | 6A | 250V | 6A | 125V | 70°C | No |
| C13 / C14 | Yes | 10A | 250V | 10A | 125V | 70°C | No |
| C15 / C16 | Yes | 10A | 250V | 10A | 125V | 120°C | No |
| C17 / C18 | No | 10A | 250V | 10A | 125V | 70°C | No |
| C19 / C20 | Yes | 16A | 250V | 20A | 125V | 70°C | No |
| C21 / C22 | Yes | 16A | 250V | 20A | 125V | 155°C | No |
While the IEC 60320 standard is widely adopted globally, it primarily focuses on specific connector types such as C13, C15, and C19. However, plug types vary widely between countries, with each often using its own unique connector designs.
NEMA
The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) defines the standard for power connectors widely used across North America. These connectors are durable and provide reliable grounding, making them suitable for both residential and industrial use.
Designed for compatibility with the 120V and 240V electrical systems in the U.S. and Canada, NEMA connectors also come in a variety of configurations, primarily straight-blade and locking connectors, to suit different applications.
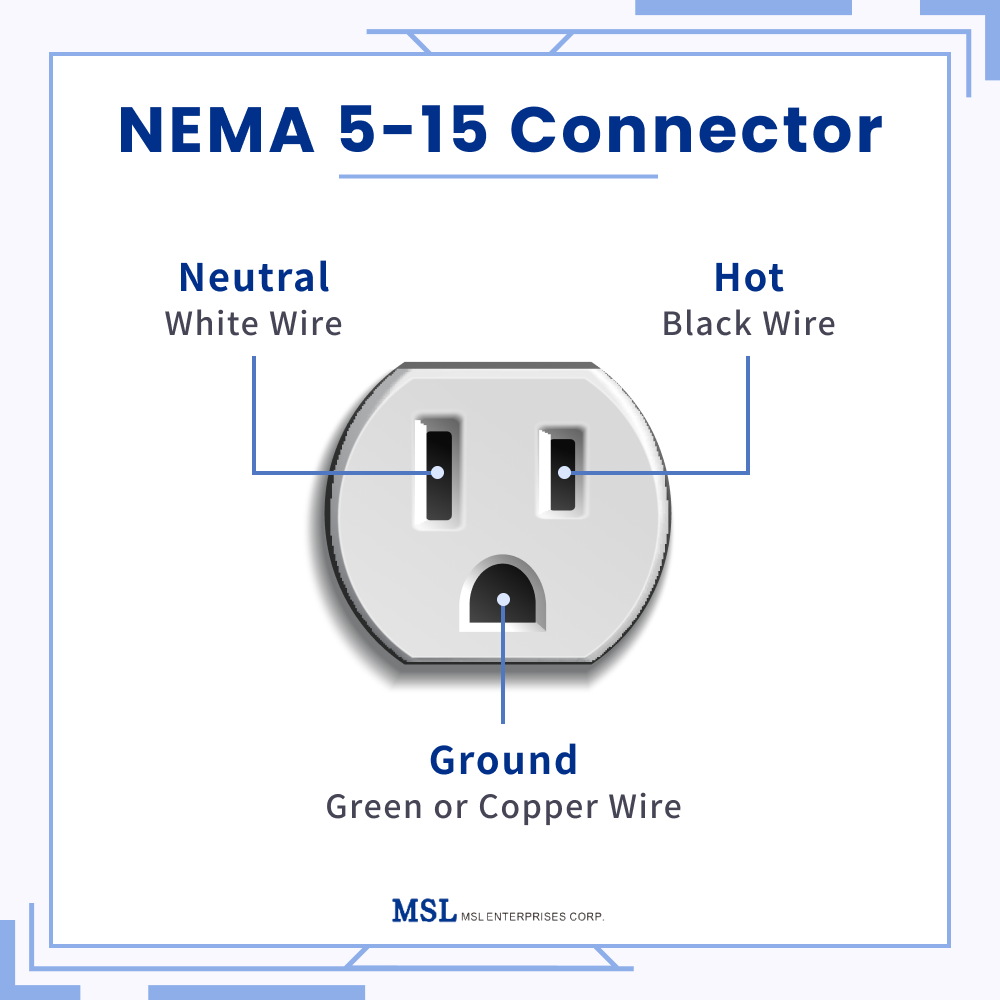
Among all of the NEMA connectors, NEMA 5-15 is the most common one in sockets with prongs specifically arranged for safety and functionality. There are 3 prongs: hot, neutral, and ground.
- Hot (Live): This prong carries the active current. In North American plugs, it’s often slightly shorter or angled compared to the neutral prong, making it easy to identify. The hot prong is responsible for delivering current to the connected device.
- Neutral: The neutral prong returns the current back to the electrical panel, completing the circuit. This prong is typically wider than the hot prong in non-polarized plugs to prevent incorrect insertion, ensuring the live connection is made only to the intended hot terminal.
- Ground: The ground prong provides an essential safety feature by directing excess current away from the device and user, protecting against electrical shocks. Ground prongs are generally round or U-shaped and are crucial in case of short circuits or electrical surges.
NEMA Straight-Blade Connectors
Straight-blade connectors are commonly found in homes and offices, recognizable by their parallel prongs.
- NEMA 1-15: A two-prong, non-grounded connector rated for 15 amps and 125 volts, often found on older devices or double-insulated appliances. It lacks a grounding pin, so it’s commonly used in low-power or insulated applications.
- NEMA 5-15: A grounded, three-prong connector also rated for 15 amps and 125 volts. This connector is standard in household items like computers and small appliances, providing a grounding pin for added safety and reducing the risk of electric shock.
- NEMA 5-20: Similar to the 5-15 but with a “T”-shaped neutral prong, rated for 20 amps and 125 volts. The 5-20 is designed for heavier equipment, such as air conditioners and power tools, where additional current capacity is needed.
- NEMA 6-15: A three-prong connector rated for 15 amps and 250 volts. Unlike the 5-series, the 6-15 operates at a higher voltage, making it suitable for devices requiring more power, such as some air conditioning units and specialized equipment in industrial settings. It has a grounding pin and two flat blades oriented in parallel.
- NEMA 6-20: Similar to the 6-15 but rated for 20 amps and 250 volts, with a “T”-shaped neutral prong to accommodate higher current. The 6-20 is commonly used for equipment like commercial-grade air conditioners, industrial machines, and other high-power appliances requiring a 250V supply.
NEMA 5-15 and NEMA 5-20 for Hospital-Grade Plugs
In medical environments, the hospital-grade version of the 5-15 plug adheres to stricter standards, featuring a green dot to signify compliance. These plugs are designed to provide consistent electrical continuity and rugged durability. They are essential for powering medical equipment such as heart monitors and infusion pumps.
Similarly, the NEMA 5-20 plug is utilized for devices requiring higher power. The hospital-grade variant ensures enhanced safety and reliability, suitable for equipment like portable X-ray machines and CT scanners.
CEE
CEE connectors, designed under the European CEE (International Commission on Rules for the Approval of Electrical Equipment) standards, are known for their enhanced safety features. With strong grounding mechanisms, they provide user protection and reliable performance, especially in high-current or high-voltage situations common in European electrical systems.
Here are some of the common CEE power connector types:
- CEE 7/4 (Type F) - "Schuko": This grounded connector is distinguished by its two round prongs and grounding clips, rated for 16A and 250V. Widely used in Germany, Austria, and the Netherlands, the "Schuko" plug powers various household appliances and electronic devices.
- CEE 7/5 (Type E): Featuring two round pins and an additional grounding socket, the CEE 7/5 connector is compatible with French-style outlets. With a 16A and 250V rating, this plug is common in France, Belgium, and Poland, offering a safe and secure connection for household equipment.
- CEE 7/7: This versatile, hybrid connector combines Type E and Type F features, with two round prongs, side grounding clips, and a grounding contact. Compatible with both outlet types, the CEE 7/7 plug is widely adopted across Europe, making it a flexible choice for different European countries.
Other Standards for Plugs
In addition to the widely recognized IEC, NEMA, and CEE standards, several countries have developed their own standards for plugs to meet specific regional requirements.
- Australia and New Zealand: Both countries utilize the Type I plug, featuring two flat pins in a V-shape and a grounding pin. This configuration is standardized under AS/NZS 3112, ensuring compatibility across both nations.
- Japan: Japan employs Type A and Type B plugs, similar to those in North America, but with a key distinction: the voltage is 100V, and the frequency varies between 50Hz and 60Hz depending on the region. This necessitates careful consideration when using electrical devices from other countries.
- Brazil: Brazil has adopted the Type N plug, characterized by two round pins and a grounding pin. This standard is unique to Brazil and a few other countries, reflecting the nation's specific electrical infrastructure.
- UK: The United Kingdom, along with Ireland and several Commonwealth countries, uses the Type G plug, defined by the BS 1363 standard. This plug features three rectangular pins arranged in a triangular pattern and includes a built-in fuse for additional safety.
- China: China uses a distinctive plug type known as Type I, similar to Australia and New Zealand, with two flat pins in a V-shape and an optional grounding pin. However, the Chinese Type I plug follows the GB 2099.1 and GB 1002 standards, with a slight difference in plug pin size and spacing.
How to Choose the Right Types of Power Cable?
Selecting the right power cable is critical for achieving optimal safety, efficiency, and durability in electrical setups. Key factors to keep in mind include:
Voltage and Current Requirements
Cables are rated for specific electrical loads. Using a cable with a lower rating can cause overheating, insulation failure, and even fire hazards. It’s important to match the cable's voltage and current capacities with your equipment to ensure safe and reliable performance. Underrated cables can’t handle excessive heat properly. For high-power applications, a thicker gauge cable may be needed to safely handle the current load.
Environmental Conditions
The environment where a power cable is installed affects its durability and performance. Temperature changes, moisture, and exposure to chemicals can damage some cable materials.
For instance, in high-temperature areas, cables need heat-resistant insulation to prevent melting or damage. In moist or chemically active environments, cables with protective sheathing, like PVC or cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), provide better resistance to corrosion and wear.
Safety Standards
Choosing cables with proper certifications helps prevent malfunctions and hazards, protecting both people and equipment in sensitive settings, like hospitals or industrial plants. Safety standards, such as IEC, NEMA, or CEE, verify that cables have undergone testing for quality and safety, including insulation strength, fire resistance, and durability. Certification marks like UL or CE also indicate adherence to these standards.
Cable Length
Cable length is an important factor because longer cables can lead to voltage drop, meaning that electricity loses some of its power as it travels over a distance. This can cause connected devices to operate less efficiently or even malfunction.
Choosing the right cable size and thickness for the required length helps minimize voltage drop to ensure stable performance. This is especially critical in situations where precise voltage is essential, such as with sensitive medical equipment.
Flexibility
Different applications need different levels of cable flexibility. Fixed installations, like in-wall or buried wiring, work best with rigid cables designed to stay in place. However, for applications with movement, like portable tools or machinery, flexible cables are necessary to prevent damage from bending. Flexible cables are also easier to install in tight spaces and can navigate complex layouts more smoothly.
Future Expansion
Choosing a cable with extra capacity helps your system handle future power needs without needing immediate upgrades. By planning for potential load increases, you create a more durable and flexible power system, saving you from frequent replacements and their associated costs. This is especially important in places like data centers or industrial facilities, where electrical demands are likely to grow.
Power Up with MSL Enterprises Corp – Your Go-To Power Cable Supplier
MSL Enterprises Corp. is the name you can trust for all your Ethernet cable needs. Since 1987, MSL has been delivering custom solutions with competitive pricing and fast lead times, making us a preferred partner for global clients. With state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities and laboratories in China and Vietnam, and ISO-certified production processes, we guarantee that your network infrastructure meets the highest industry standards.
Our robust manufacturing setup, featuring multiple production lines and state-of-the-art fiber assembly technology, allows us to offer customized solutions that meet even the most specific requirements. Whether you require reliable cables for everyday office setups or robust, high-speed networks, contact us today to discover the perfect solution for your business needs.